
Total Hip Replacement Surgeon in Palm Beach Gardens, FL
Joint conditions such as arthritis may cause damage to the cartilage and bones leading to chronic pain in the hip and/or disability. The condition can be treated by replacing the damaged parts with artificial components. Dr. Robert Avino provides expert diagnosis and hip replacement surgery in Palm Beach Gardens, FL. Dr. Robert Avino also provides the highly specialized care during and after the surgery. Contact Dr. Robert Avino’s office for an appointment today!
If your hip has been damaged by arthritis, a fracture, or other conditions, activities like walking or putting on shoes may become painful and difficult. Medications, lifestyle changes, or walking aids might not always provide enough relief.
Total hip replacement surgery is a safe and effective solution to reduce pain, restore motion, and help you return to daily activities. Advances in surgical techniques and technology since the 1960s have made this one of the most successful procedures, with over 450,000 performed annually in the U.S.
Hip Anatomy
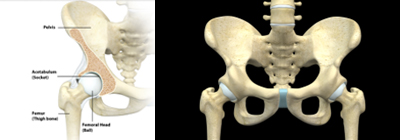
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint, one of the body's largest joints.
The acetabulum forms the socket, part of the pelvis bone, while the femoral head (upper femur) forms the ball. Smooth articular cartilage covers these surfaces, cushioning the bones and enabling smooth movement.
A synovial membrane surrounds the joint, producing fluid that lubricates the cartilage and reduces friction. Ligaments connect the ball to the socket, providing joint stability.
Common Causes of Hip Pain
The most common cause of chronic hip pain and disability is arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and posttraumatic arthritis.
- Osteoarthritis: Age-related wear-and-tear arthritis, common in those 50+ or with a family history. Cartilage wears away, causing bones to rub together, leading to pain and stiffness. Childhood hip irregularities can also contribute.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disease where inflammation damages cartilage, causing pain and stiffness. It’s the most common type of inflammatory arthritis.
- Posttraumatic Arthritis: Develops after a serious hip injury or fracture, with damaged cartilage leading to pain and stiffness over time.
- Osteonecrosis: Limited blood supply to the femoral head from injury or disease can collapse bone surfaces, causing arthritis.
- Childhood Hip Disease: Hip problems in infancy or childhood, even if treated, can lead to arthritis later due to abnormal joint growth.
What is Total Hip Replacement?
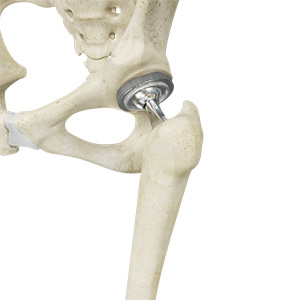
In a total hip replacement (also called total hip arthroplasty), the damaged bone and cartilage is removed and replaced with prosthetic components.
- The damaged femoral head is removed and replaced with a metal stem that is placed into the hollow center of the femur. The femoral stem may be either cemented or "press fit" into the bone.
- A metal or ceramic ball is placed on the upper part of the stem. This ball replaces the damaged femoral head that was removed.
- The damaged cartilage surface of the socket (acetabulum) is removed and replaced with a metal socket. Screws or cement are sometimes used to hold the socket in place.
- A plastic, ceramic, or metal spacer (also called a liner) is inserted between the new ball and the socket to allow for a smooth gliding surface.
Is Total Hip Replacement Surgery for You?
The decision to have total hip replacement surgery should be a co-operative one made by you, your family, your primary care doctor, and your orthopaedic surgeon. The process of making this decision typically begins with a referral by your primary care doctor to an orthopaedic surgeon for an initial evaluation.
When Surgery Is Recommended
There are several reasons why your orthopaedic surgeon may recommend total hip replacement surgery. People who benefit from hip replacement surgery often have:
- Hip pain that limits everyday activities, such as walking or bending
- Hip pain that continues while resting, either during the day or at night
- Stiffness in a hip that limits the ability to move or lift the leg
- Inadequate pain relief from anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy, or walking supports
Candidates for Surgery
There are no absolute age or weight restrictions for total hip replacements.
Recommendations for surgery are based on a patient's pain and disability, not age. Most patients who undergo total hip replacement are 50 to 80 years old, but orthopaedic surgeons evaluate patients individually. Total hip replacements have been performed successfully at all ages, from the young teenager with juvenile arthritis to the elderly patient with degenerative arthritis.
The Orthopaedic Evaluation
An evaluation with an orthopaedic surgeon consists of several components:
- Medical history: Your orthopaedic surgeon will gather information about your general health and ask questions about the extent of your hip pain and how it affects your ability to perform everyday activities.
- Physical examination: This will assess hip mobility, strength, and alignment.
- X-rays: These images help to determine the extent of damage or deformity in your hip.
- Other tests: Occasionally other tests, such as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, may be needed to determine the condition of the bone and soft tissues of your hip.
Deciding To Have Total Hip Replacement Surgery
Consultation with Dr. Avino
Dr. Avino will discuss whether total hip replacement is the best option for relieving your pain and improving mobility. Other treatments, such as medications, physical therapy, or different surgeries, may also be considered.
Dr. Avino will explain potential risks and complications, both during and after surgery.
Ask questions whenever needed. Understanding the procedure helps you better manage the changes it brings to your life.
Realistic Expectations
Most patients experience significant pain relief and improved ability to perform daily activities.
Over time, the implant may wear, and excessive activity or excess weight can accelerate this process, potentially causing pain or loosening.
Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, golf, biking, and hiking are encouraged, while high-impact sports are discouraged.
With proper activity adjustments, hip replacements can last for many years.
Possible Complications of Surgery
The complication rate following total hip replacement surgery is low. Serious complications, such as joint infection, occur in less than 2% of patients. Major medical complications, such as heart attack or stroke, occur even less frequently. However, chronic illnesses may increase the potential for complications. Although uncommon, when these complications do occur, they can prolong or limit full recovery. Possible complications include:
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Leg-length inequality
- Dislocation
- Loosening and implant wear
- Nerve and blood vessel injury
- Bleeding
- Fracture
- Stiffness.
- A small number of patients continue to experience pain after surgery.
Preparing for Total Hip Replacement Surgery
Medical Evaluation
Before surgery, your orthopedic surgeon may require a full physical exam to ensure you're fit for the procedure and recovery. Patients with chronic conditions like heart or kidney disease may need specialist evaluations.
Tests
Blood tests, urine tests, an EKG, and chest X-rays may be needed to prepare for surgery.
Skin Preparation
Report any skin irritations, such as rashes or cuts, as these can increase infection risks. Surgery may be postponed if an infection is present.
Medications
Inform your surgeon about all medications. They’ll advise which ones to stop or continue before surgery.
Weight Loss
If overweight, your doctor may recommend weight loss to reduce stress on your new hip and lower surgical risks.
Dental and Urinary Evaluations
Complete major dental work before surgery to prevent infection risks. For recurring urinary issues or prostate conditions, consider treatment beforehand.
Social and Home Planning
Arrange help for daily tasks like cooking or bathing during recovery. Home adjustments, such as safety bars, raised toilet seats, and removal of loose carpets, can aid mobility and safety.
What to Expect During Your Total Hip Replacement Procedure
Depending on your plan, you will either stay at the hospital overnight or go home the same day (same-day surgery).
Anesthesia
Common options include:
- General anesthesia (you’re asleep)
- Spinal, epidural, or nerve block anesthesia (numb from the waist down)
Implant Components
Hip implants have two components:
- Ball: Made of metal or ceramic
- Socket: Made of plastic, ceramic, or metal
Components may be press-fit for bone growth or cemented, depending on bone quality. Your surgeon will choose the best option for you.
The surgery typically takes 1–2 hours. Damaged bone and cartilage are replaced with implants to restore hip function. After surgery, you’ll recover in the recovery room before being moved to a hospital room or discharged home.
Recovery after Total Hip Replacement
Pain Management: Short-term pain relief may involve opioids, NSAIDs, acetaminophen, or local anesthetics. Use opioids only as directed and stop as pain improves.
Wound Care: Stitches or staples will be removed in 2 weeks. Keep the wound dry until sealed and bandage as needed.
Diet: A balanced diet with fluids supports healing. Appetite loss is common initially.
Activity: Gradually increase mobility with walking and exercises to restore strength and flexibility. Resume normal light activities within 3–6 weeks.
Avoiding Problems: Prevent blood clots by following your surgeon's advice on blood thinners. Watch for calf pain, swelling, shortness of breath, or fever. Prevent infections with proper hygiene and, if needed, antibiotics before procedures.
Avoiding Falls: Use assistive devices like walkers or canes until strength and balance improve.
If you would like to have additional information on the treatment of hip arthritis or would like to learn more about total hip replacement, please contact Dr. Robert Avino, serving the communities of Palm Beach Gardens, FL.









